
This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors.
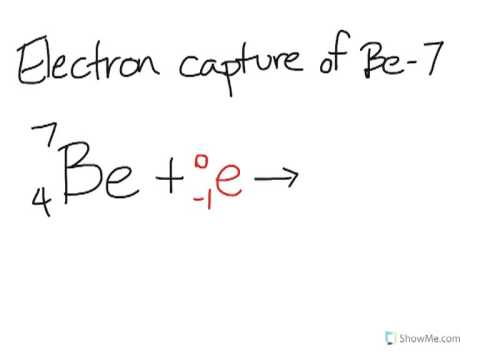
This process involves emission of high energy gamma rays from the nucleus. Shop by Category Find the Best TVS & Audio/Video Equipment at Costco Capture Lifes Important Moments with Cameras & Camcorders Enjoy the Latest Video Games. Electron capture is one form of radioactivity.A parent nucleus may capture one of its orbital electrons and emit a neutrino. A nucleus rich in protons absorbs an inner electron from the atom. Proton-deficient nuclei undergo beta decay - emitting a beta particle (electron) and an antineutrino to convert a neutron to a proton - thus raising the elements atomic number Z by one.This chapter is devoted to consideration of electron capture (EC), which is one of the most important recombination mechanisms in collisions of ions with various targets. Answer Verified 261.3k + views Hint: Electron capture is a nuclear process. Types of Particles in Nuclear Reactions Many entities can be involved in nuclear reactions. Proton-deficient or neutron-deficient nuclei undergo nuclear decay reactions that serve to correct unbalanced neutron/proton ratios. To describe a nuclear reaction, we use an equation that identifies the nuclides involved in the reaction, their mass numbers and atomic numbers, and the other particles involved in the reaction.

Other heavy unstable elements undergo fission reactions in which they split into nuclei of about equal size. Alpha decay is a form of spontaneous fission, a reaction in which a massive nuclei can lower its mass and atomic number by splitting. The energy released in an alpha decay reaction is mostly carried away by the lighter helium, with a small amount of energy manifesting itself in the recoil of the much heavier daughter nucleus. (a) What other particle or particles are emitted in the decay (b) Assume that the electron is captured from the K shell. Therefore, the mass of the parent atom must simply be greater than the sum of the masses of its daughter atom and the helium atom. Since the number of total protons on each side of the reaction does not change, equal numbers of electrons are added to each side to make neutral atoms. \( \newcommand\]Īs with beta decay and electron capture, Δm must only be less than zero for spontaneous alpha decay to occur.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
